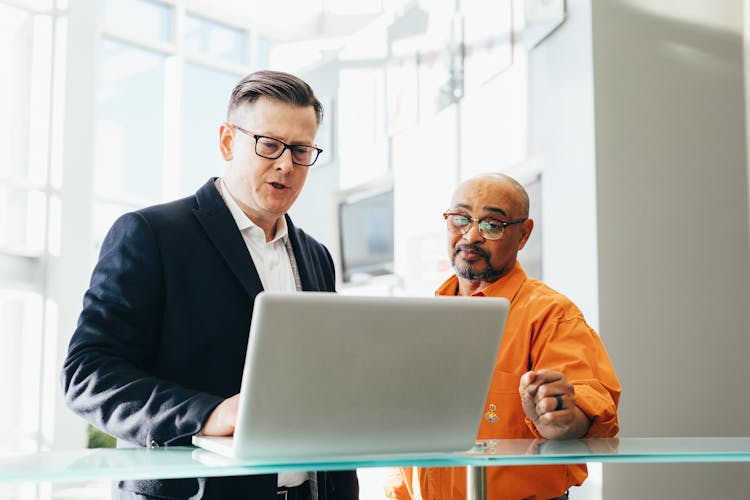
Private Placement Programs are high-profit investment programs. They are safe, private, “invitation only” trading programs for financial instruments (especially MTNs) offered by the world’s leading banks to help their clients finance capital investment, expansion, and specific projects.
Investors first buy these instruments early after issuance with a significant discount from their nominal value. Afterwards they are sold in the secondary market at a higher price. The difference between the purchase and selling prices is the investor’s profit. PPPs are offered only to customers with high purchasing power and such transactions may only be carried out by licensed dealers.
For example, you as an individual can agree to loan $100 to a friend with the understanding that the interest for the loan will be 10%, resulting in a total of $110 to be repaid. Effectively, you have created $10, even though that money can not be seen initially. Banks do this sort of lending every day, even though the amounts run into the billions of dollars, with the amounts of interest involved, and potential profits in the PPP market, correspondingly higher. PPPs involve trading these discounted bank-issued debt instruments which defer payment obligations, or debts.
The PPP market is changing and it is no longer limited to governments and MTNs. It is common practice for large, stable companies of all types to issue their own debt instruments.
Every day, the world’s major banks issue billions of dollars worth of instruments such as Medium Terms Notes (MTN), Bank Guarantees (BG), and Stand-By Letters of Credit (SBLC), many of which are sold on the secondary market at discounted prices.
All trading programs in the PRIVATE PLACEMENT PROGRAM area include trading with discounted debt notes. Furthermore, in order to bypass the legal restrictions, this trading can only be done on a private level. This is the main difference between trading with PPP and “normal” trading, which is highly regulated. PRIVATE PLACEMENT level business transactions are free from the usual restrictions in the securities market. It is based on reliable, essential, special relationships and protocols.
However, none of these programs can be started unless there are sufficient funds to support each transaction. The banks need to “share the wealth” by allowing private investors to participate in the investment, in order to help the bank increase its own investment reach.